However, standard costs also create the potential for managers to manipulate or inflate financial data to meet their targets. Some managers may withhold important information about operational problems, for example, or intentionally overstate revenues to appear more successful. Standard costs need to be carefully managed to avoid encouraging unethical behavior. However, standard costs can also have unintended consequences, focusing on short-term results at the expense of more strategic considerations.
Standard cost yield variance- Recommended Reading
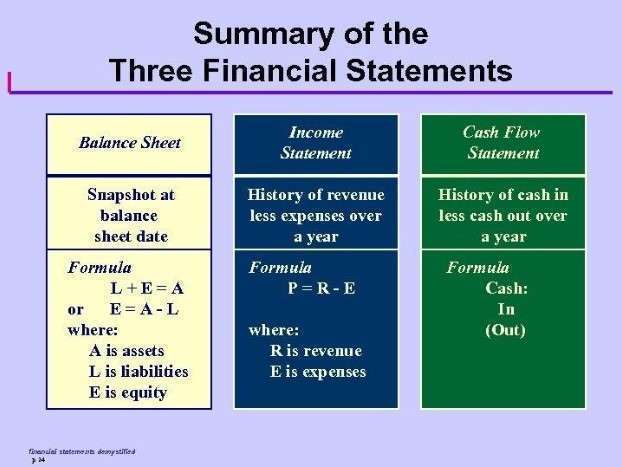
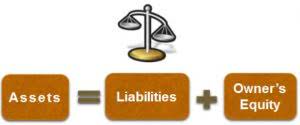
They cannot completely picture a company’s financial health or overall success. Instead, they should be viewed with other financial indicators to better understand a company’s financial situation. Document your standards comprehensively with standard cost sheets detailing the components of each product’s cost. This transparency prevents the “black box” syndrome where nobody trusts the numbers standard costing system because they don’t understand where they came from.
Direct Labor
- The primary goal of calculating and using standard costs is to set objectives and reach specific targets.
- This enables management to investigate discrepancies promptly and take corrective actions, such as optimizing production methods or renegotiating supplier contracts.
- The manufacturing overhead variances were the differences between the accounts containing the actual costs and the accounts containing the applied costs.
- An unfavorable variance involves spending more, or using more, than the anticipated or estimated standard.
Another way to determine if a standard cost is fair is to compare it to the normal balance costs of similar products. If the standard cost is significantly lower than the competition, it may be too low and needs to be raised. A positive cost variance happens when actual expenses are less than budgeted expenses.
Direct labor consists of a standard amount of work and a standard rate per hour of work.

Ideal standards, also called perfection standards, are established at a maximum efficiency level with no unplanned work stoppages. In setting standards, the critical question is deciding on the standard type to fix the cost. If the net realizable value of the inventory is less than the actual cost of the inventory, it is often necessary to reduce the inventory amount. Carefully planned and operated procedures, as required under this system in respect of recording of prices, time, quantities etc. might not have been adopted. A toning up of the variance analysis system can obviate this difficulty. Standard costing may be found unsuitable and costly in the case of industries dealing with non-standard products and repair jobs which keep on changing in accordance with customers’ specifications.
Four benefits of standard costs
- Practical standards consider employee breaks, machine downtime, and employees’ varying productivity levels.
- This can lead to managers making decisions based on inaccurate cost information.
- In other words, the balance sheet will report the standard cost of $10,000 plus the price variance of $3,500.
- Otherwise, they may have inaccurate cost information, leading to poor decision-making and sub-standard products or services.
- The standards are not so high that employees will not try to reach them and not so low that they do not give any incentive for employees to achieve profitability.
- For example, let’s say a company sets a standard cost of $10 per unit for a particular product, based on expected materials, labor, and overhead costs.
It can assess the efficiencies or inefficiencies that caused the variations and make the necessary adjustments. A manufacturer may use standard costs to carefully project costs for the following fiscal year and then compare the actual costs to those projections. The company is on track to meet the cost component of its profit plan if the actual costs are comparable to the standard costs (the planned costs; what the costs should be). However, if actual costs are consistently changing, it might be necessary to update standard costs frequently. It is simplest to regularly update costs for the most expensive Accounting for Churches inventory items while deferring cost updates for lesser-priced items.
Explore the essentials of standard costing, from key components and calculations to its impact on budgeting and financial statements. Standard costing is fated to disappear into history like many other tools and techniques that were once useful but have now been replaced by something better (and less expensive!). So standard costing has gone the way of standard time/level of service, standard-costing reports, and standard staff numbers. When investigating variances in standard costs, there are vital tips to keep in mind to ensure accuracy and completeness in your findings. Standard cost can help decision-makers compare the relative costs of different options and choose the option that is most likely to minimize total costs. Sometimes, standard cost may also be used to negotiate better terms with suppliers.
